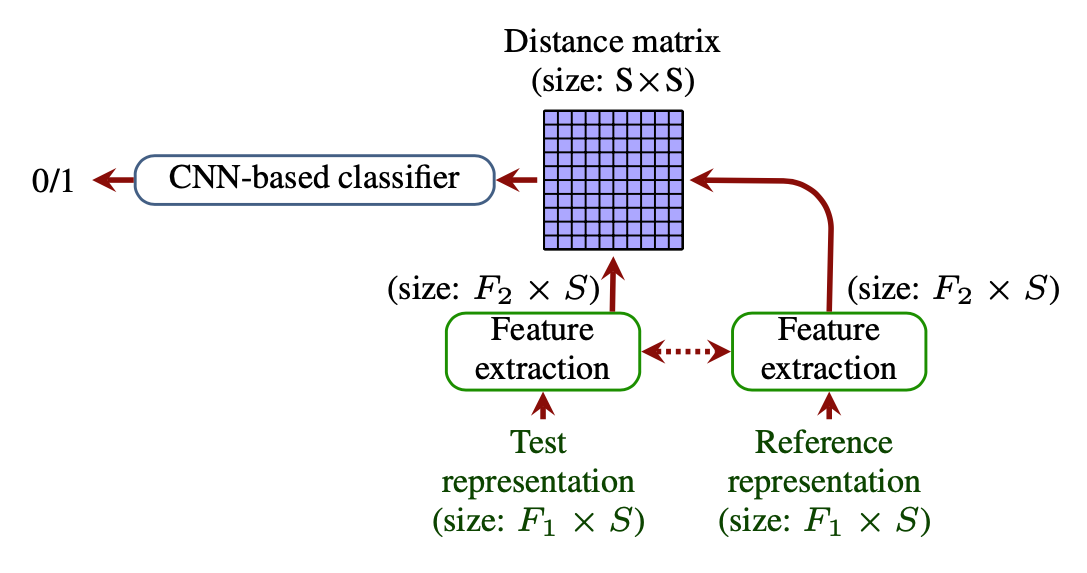
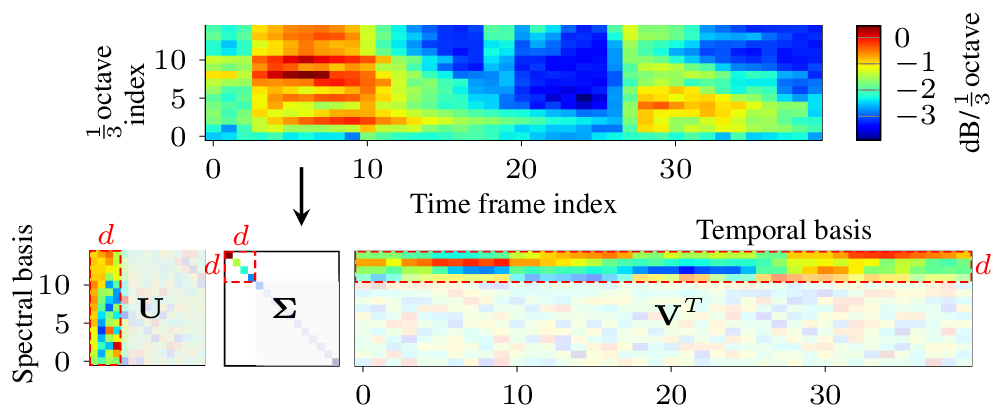
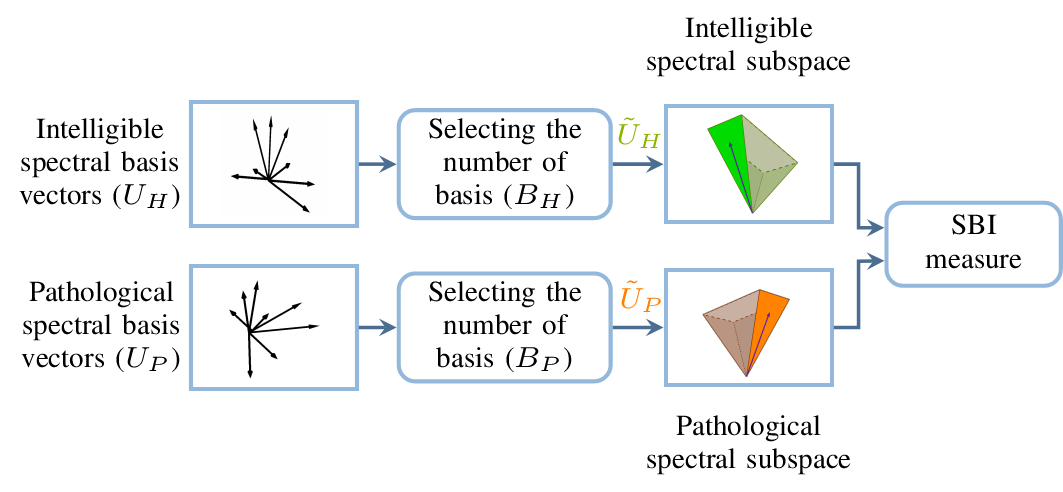
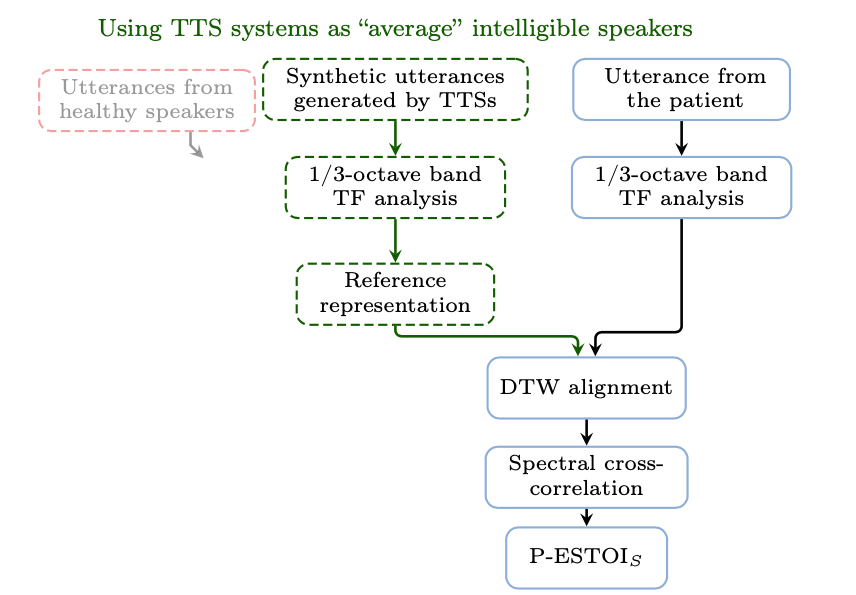
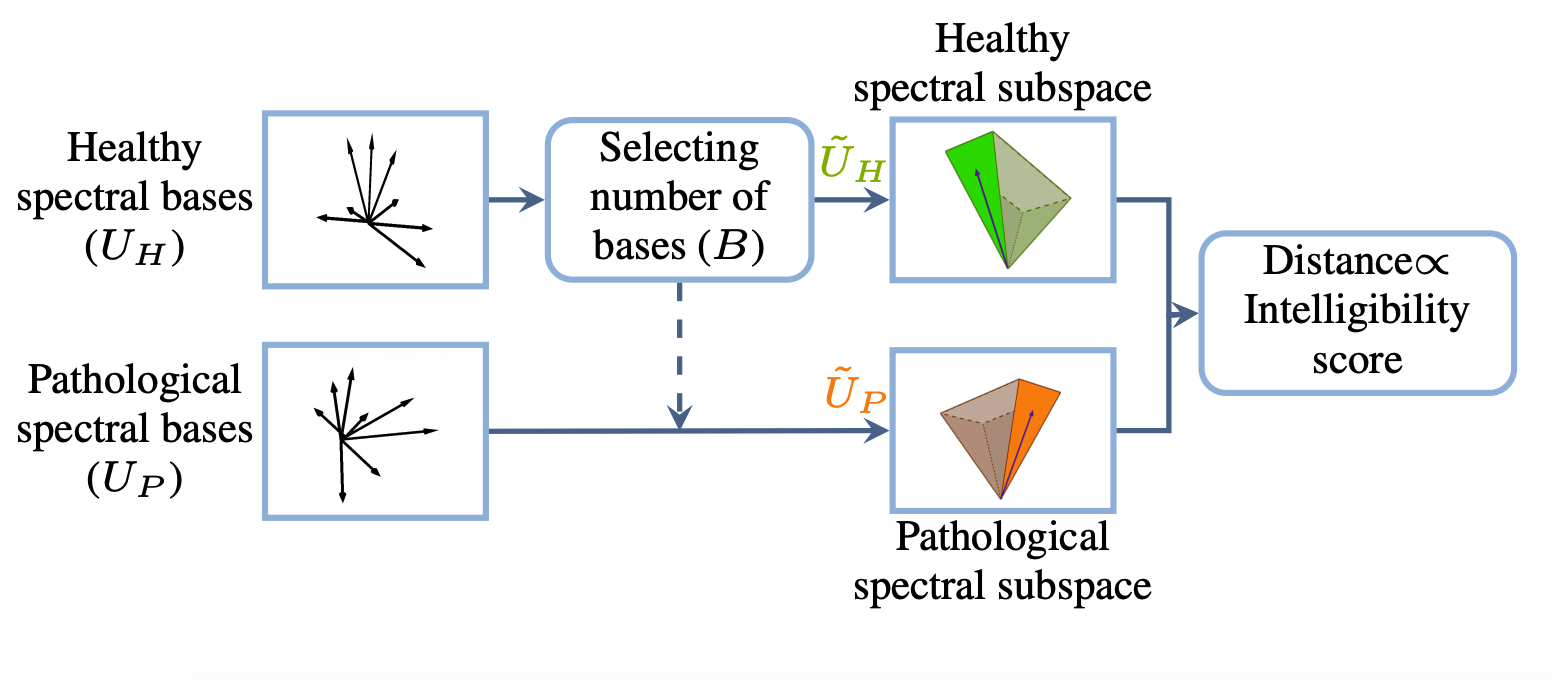
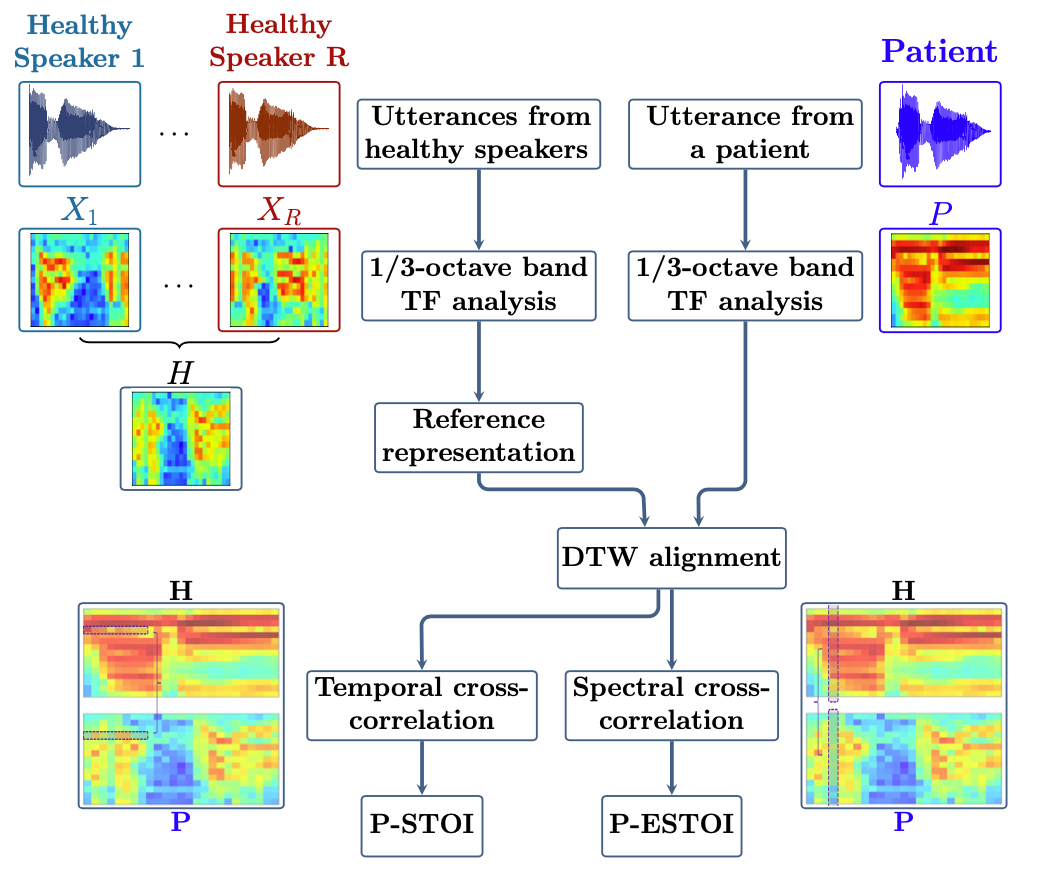
On using the UA-Speech and TORGO databases to validate automatic dysarthric speech classification approaches
ICASSP, 2023
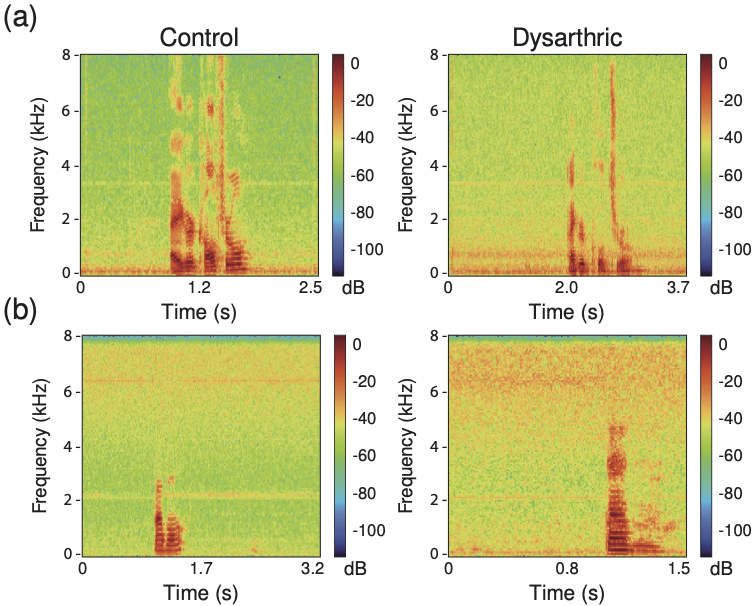
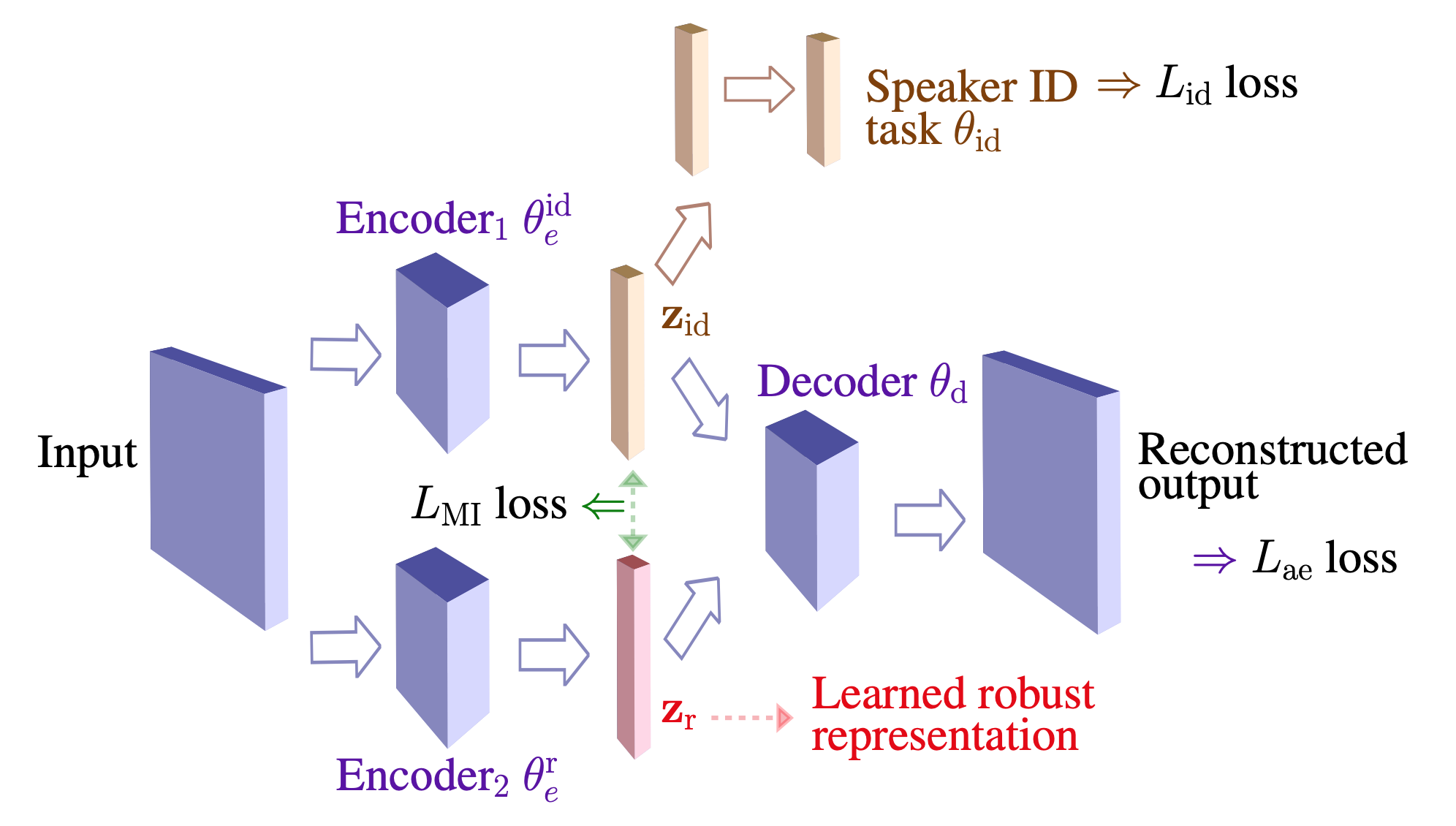
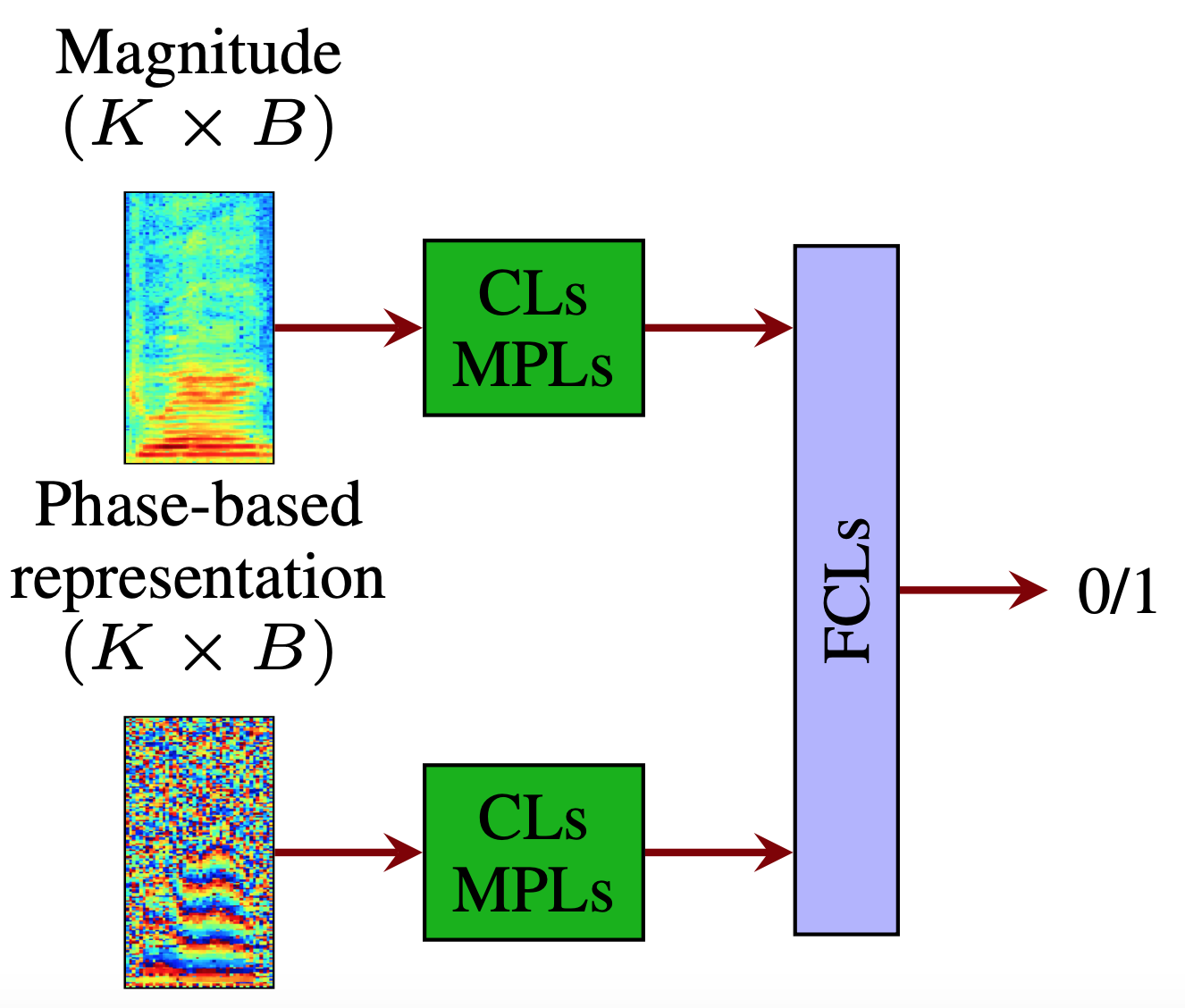
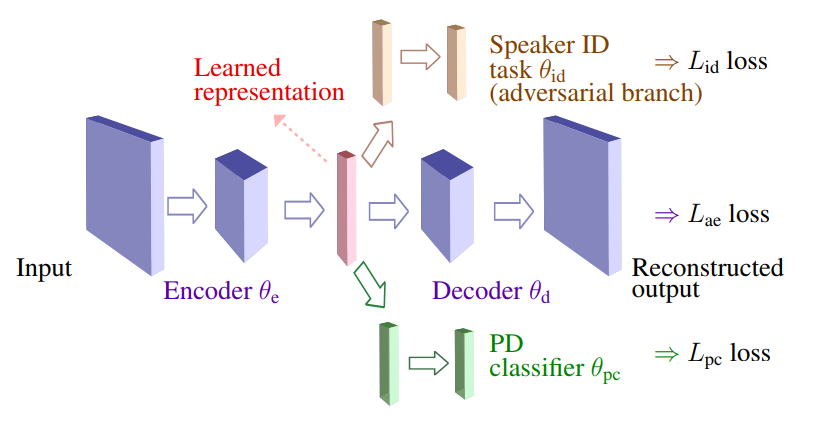
Abstract: Although the UA-Speech and TORGO databases of control and dysarthric speech are invaluable resources made available to the research community with the objective of developing robust automatic speech recognition systems, they have also been used to validate a considerable number of automatic dysarthric speech classification approaches. Such approaches typically...
[Read More]